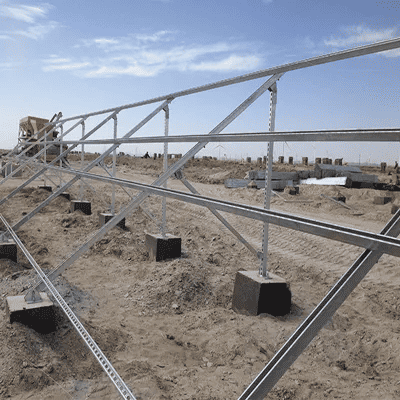
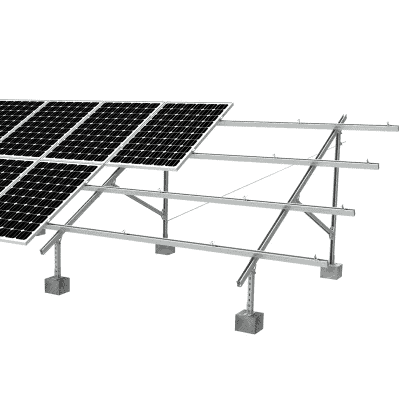

Solar Mounting Structure
These are the support structures that secure solar panels to either a roof, a wall, or to the ground. They are often adjustable to ensure the panels are optimally tilted towards the sun for maximum energy production.
The choice of the most appropriate solar mounting system depends on various factors such as location, installation surface, local weather conditions, budget, and so on.
There are several types of solar mounting structures:
Fixed Mounts: These are used when panels are installed on rooftops or ground-mounted solar installations. As the name suggests, the panels are fixed and can’t be adjusted to follow the sun’s movement.
Adjustable Mounts: These allow the tilt angle of the solar panels to be adjusted. This can be useful in locations where the angle of the sun changes significantly with the seasons.
Tracking Mounts: These are the most advanced and expensive type of mount. They move to follow the sun throughout the day which maximizes the amount of sunlight the panels receive.
Pole Mounts: These are used to attach panels to a single pole, raising them off the ground. This can be useful in areas with heavy snow or for installations where shading is a concern.
Ballasted Mounts: These are used for flat roofs or ground-mounted systems where it’s not desirable to penetrate the installation surface with bolts. Instead, the system is held down with weights (ballast).
Ground Mounts: These are used when panels are installed on the ground, and they come in standard, pole-mount, and tracking configurations.
Roof Mounts: These are designed to attach directly to the roof structure, and they can be used on a variety of roof types.
These systems are usually made from aluminum, stainless steel, or a combination of both. They need to be durable and resistant to corrosion to withstand outdoor conditions for many years.
Our commitment to quality, safety, and cost efficiency sets us apart in the industry. As dedicated partners, we support clients of all sizes worldwide. Whether you need a reliable aluminum ringlock ledger or other scaffolding solutions, we are here to meet your needs with unparalleled expertise and dedication.
Our aluminum ringlock scaffolding systems are not only lightweight and durable but also adhere to the highest safety standards. These features make them the ideal choice for a wide range of construction and industrial projects. We are consistently dedicated to providing top-quality products and services, ensuring your projects proceed smoothly and cost-effectively.

Jumply Scaffolding brings extensive experience and state-of-the-art automated equipment to deliver customized scaffolding solutions, including ringlock ledger systems, tailored to meet diverse requirements.
Jumply stands for safety and quality in scaffolding, showcased through our construction projects. Experience the superior quality of our products, including our ringlock ledger systems, which we continually enhance to meet your needs.
Jumply Solar Mounting Structure
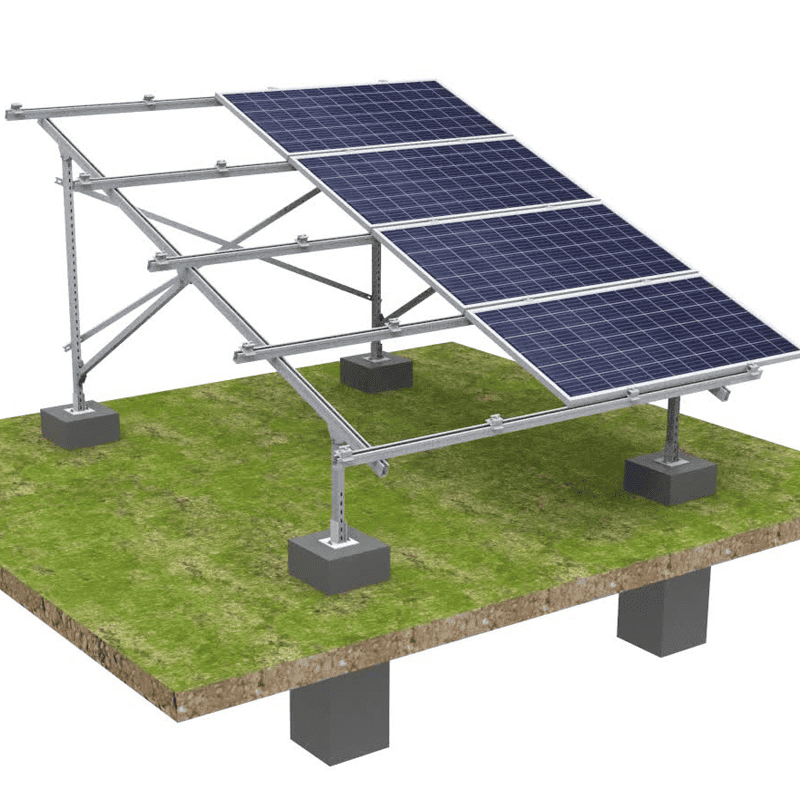
Specification
| Mounting Type | Typical Material | Typical Size (Length x Width) | Other Features |
| Fixed Mounts | Aluminum, Stainless Steel | 65 x 39 inches (for one standard solar panel) | Non-adjustable, sturdy design |
| Adjustable Mounts | Aluminum, Stainless Steel | 65 x 39 inches (for one standard solar panel) | Allows changing of panel tilt |
| Tracking Mounts | Aluminum, Stainless Steel | 65 x 39 inches (for one standard solar panel) | Follows the sun’s path |
| Pole Mounts | Aluminum, Stainless Steel | 65 x 39 inches (for one standard solar panel) | Raises panels off the ground |
| Ballasted Mounts | Aluminum, Stainless Steel | 65 x 39 inches (for one standard solar panel) | Uses weights for stability |
| Ground Mounts | Aluminum, Stainless Steel | 65 x 39 inches (for one standard solar panel) | Suitable for non-roof installations |
| Roof Mounts | Aluminum, Stainless Steel | 65 x 39 inches (for one standard solar panel) | Designed for various roof types |
The size provided here, 65 x 39 inches, is a very rough average for a single solar panel. The size of the mounting structure will depend on the number of panels to be installed.
In terms of material, the most commonly used are aluminum and stainless steel due to their resistance to rust and corrosion, as well as their structural strength. However, the specific grade of these materials can vary, as can the thickness and other features, depending on the manufacturer and the specific product.
Keep in mind that If you need detailed specifications for a specific product or manufacturer, it would be best to contact us.
Understanding Solar Mounting Structures: A Comprehensive Guide
Solar mounting structures are an essential component of any solar power system. They secure solar panels either to a roof, a wall, or to the ground, ensuring that the panels stay in place and are optimally tilted towards the sun for maximum energy production. But what exactly are solar mounting structures and what are the different types available? This article provides an in-depth look into solar mounting structures, aiming to answer all the questions you might have about them.
A solar mounting structure primarily serves to position the solar panels correctly with respect to the sun. This positioning directly influences the efficiency of the solar energy system. The mounting system also provides a stable and secure foundation for the solar panels, protecting them from adverse weather conditions.
There are several types of solar mounting structures available, including fixed mounts, adjustable mounts, tracking mounts, pole mounts, ballasted mounts, ground mounts, and roof mounts. Each type has its own set of advantages and is suitable for specific situations.
Fixed mounts are the most basic type of mounting structure. They secure the panels in a fixed position, typically optimally angled towards the sun. On the other hand, adjustable mounts allow the tilt angle of the panels to be changed, accommodating for the changing position of the sun throughout the year.
Tracking mounts are a more advanced option that follows the sun’s path throughout the day, maximizing sunlight exposure. Pole mounts elevate panels off the ground, proving useful in areas with heavy snow or where shading is a concern.
For installations where it’s not preferable to penetrate the installation surface, ballasted mounts can be used. These are typically used for flat roofs or ground-mounted systems and are held down with weights.
Ground mounts and roof mounts are two broad categories. As their names suggest, ground mounts are designed for installations on the ground, and roof mounts are designed to attach directly to various types of roof structures.
These mounting systems are usually made from aluminum or stainless steel for their strength and resistance to rust and corrosion.
Remember, choosing the right solar mounting structure depends on multiple factors like your location, the installation surface, local weather conditions, and your budget. A solar energy professional can help determine the best option for your specific needs.
In conclusion, solar mounting structures play a pivotal role in any solar energy system. Understanding their purpose and the different types available helps in making informed decisions about your solar installation.
The Applications of Solar Mounting Structures: Your Key to Solar Efficiency
The role of solar mounting structures in a solar energy system is crucial, influencing both the stability and the efficiency of the system. In this guide, we’ll explore the various applications of these mounting structures in a step-by-step format, aiming to answer your common questions and help you get the most out of your solar installation.
Fixed Mounts: One of the most straightforward types of solar mounting structures, fixed mounts hold solar panels at a fixed angle. They are primarily used in residential rooftop solar installations and are designed for optimal exposure to the sun throughout the year.
Adjustable Mounts: Adjustable mounts are more flexible than fixed mounts, allowing for the tilt angle of the panels to be adjusted as per the sun’s seasonal positions. They’re excellent for maximizing solar efficiency all year round and find application in both residential and commercial installations.
Tracking Mounts: Tracking mounts are designed to follow the sun’s path throughout the day. While these mounts are typically more expensive, they’re highly efficient and are a preferred choice for large-scale commercial and utility-scale solar installations.
Pole Mounts: Pole mounts elevate solar panels off the ground, making them especially useful in areas with heavy snowfall or where shading is a concern. These mounts are a great choice for rural or remote areas where rooftop installation may not be feasible.
Ballasted Mounts: Ballasted mounts use weights to provide stability. They’re commonly used on flat roofs or ground-mounted systems where surface penetration is not desirable, making them popular for commercial buildings with flat roofs.
Ground Mounts: As the name suggests, ground mounts are designed for installations on the ground. They are often used in agricultural settings or any location where a sufficient ground area is available for solar installation.
Roof Mounts: Roof mounts are designed to attach directly to various types of roof structures. They’re prevalent in both residential and commercial solar applications due to the extensive roof space often available.
Understanding these applications can greatly assist in choosing the right solar mounting structure for your specific needs. It’s essential to note that each mount type should be made from durable materials, typically aluminum or stainless steel, to withstand weather conditions and offer long-lasting service.
FAQ
Solar mounting structures are the support systems that secure solar panels to a roof, wall, or the ground. They position the panels in an optimal angle to absorb the most sunlight and convert it into electricity.
Solar mounting structures are usually made from durable, weather-resistant materials such as aluminum or stainless steel. These materials are chosen for their strength, longevity, and resistance to corrosion.
There are several types of solar mounting structures, including fixed mounts, adjustable mounts, tracking mounts, pole mounts, ballasted mounts, ground mounts, and roof mounts. Each type serves a specific purpose and is suitable for certain applications.
Choosing the right solar mounting structure depends on various factors like your location, the installation surface, local weather conditions, and your budget. A solar energy professional can help determine the best option for your specific needs.
Adjustable mounts allow for the tilt angle of the panels to be changed according to the sun’s seasonal positions. This helps in maximizing solar efficiency throughout the year.
Tracking mounts, which follow the sun’s path throughout the day, can increase the amount of sunlight your panels receive. This can result in higher energy production. However, they are typically more expensive. Whether they are a worthwhile investment depends on your specific circumstances, such as your budget, energy needs, and geographic location.
Yes, solar mounting structures are designed to be durable and withstand various weather conditions. They are typically made from materials like aluminum and stainless steel, which are resistant to rust and corrosion.
Ballasted mounts are designed for flat roofs or ground-mounted systems where it’s not desirable to penetrate the installation surface. They use weights (ballast) to provide stability. They’re often used for commercial installations with flat roofs.
While it’s technically possible to install solar mounting structures yourself, it’s generally recommended to have a professional do it. This ensures the structure is installed securely and optimally for the best performance and longevity of your solar energy system.
Solar mounting structures typically require minimal maintenance. However, it’s a good idea to check them periodically for any signs of wear or damage. If your system uses moving parts (like in tracking mounts), those parts may need occasional lubrication or replacement.



